Triangles | Maths | Class 10th | Chapter 6 | PYQ Level 2
Triangles:- PYQ :- Level 2
Question 1.
If ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR, perimeter of ∆ABC = 32 cm, perimeter of ∆PQR = 48 cm and PR = 6 cm, then find the length of AC. (2012)
Solution:
∆ABC ~ ∆PQR …[Given
Question 2.
∆ABC ~ ∆DEF. If AB = 4 cm, BC = 3.5 cm, CA = 2.5 cm and DF = 7.5 cm, find the perimeter of ∆DEF. (2012, 2017D)
Solution:
∆ABC – ∆DEF …[Given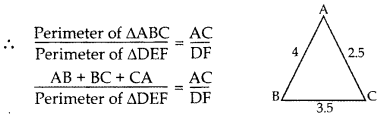
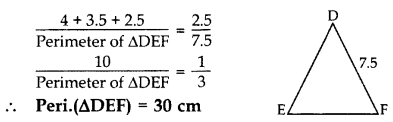
Question 3.
If ∆ABC ~ ∆RPQ, AB = 3 cm, BC = 5 cm, AC = 6 cm, RP = 6 cm and PQ = 10, then find QR. (2014)
Solution:
∆ABC ~ ∆RPQ …[Given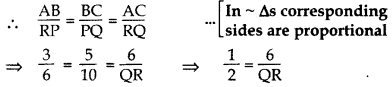
∴ QR = 12 cm
Question 4.
In ∆DEW, AB || EW. If AD = 4 cm, DE = 12 cm and DW = 24 cm, then find the value of DB. (2015)
Solution:
Let BD = x cm
then BW = (24 – x) cm, AE = 12 – 4 = 8 cm
In ∆DEW, AB || EW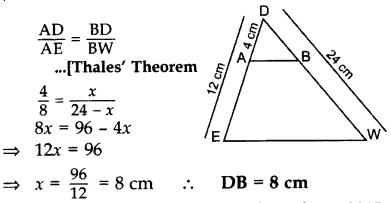
Question 5.
In ∆ABC, DE || BC, find the value of x. (2015)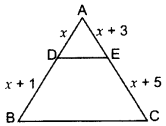
Solution:
In ∆ABC, DE || BC …[Given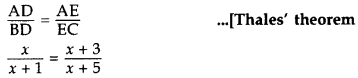
x(x + 5) = (x + 3)(x + 1)
x2 + 5x = x2 + 3x + x + 3
x2 + 5x – x2 – 3x – x = 3
∴ x = 3 cm
Question 6.
In the given figure, if DE || BC, AE = 8 cm, EC = 2 cm and BC = 6 cm, then find DE. (2014)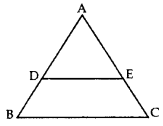
Solution:
In ∆ADE and ∆ABC,
∠DAE = ∠BAC …Common
∠ADE – ∠ABC … [Corresponding angles
∆ADE – ∆ΑΒC …[AA corollary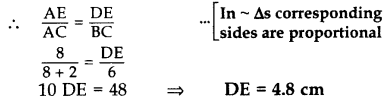
Question 7.
In the given figure, XY || QR, 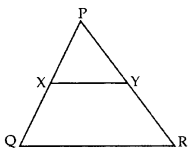
Solution:
Let YR = x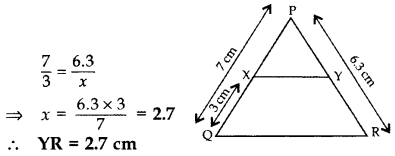
Question 8.
The lengths of the diagonals of a rhombus are 24 cm and 32 cm. Calculate the length of the altitude of the rhombus. (2013)
Solution:
Diagonals of a rhombus are ⊥ bisectors of each other.
∴ AC ⊥ BD,
OA = OC =
OB = OD =
In rt. ∆BOC,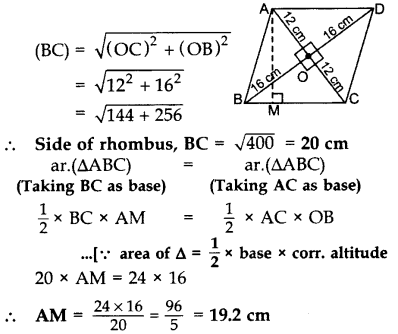
Question 9.
If PQR is an equilateral triangle and PX ⊥ QR, find the value of PX2. (2013)
Solution:
Altitude of an equilateral ∆,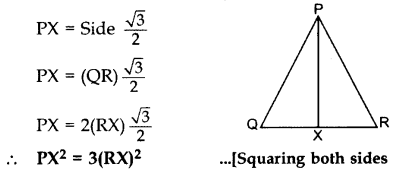
Triangles Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-I (2 Marks)
Question 10.
The sides AB and AC and the perimeter P, of ∆ABC are respectively three times the corresponding sides DE and DF and the perimeter P, of ∆DEF. Are the two triangles similar? If yes, find
Solution:
Given: AB = 3DE and AC = 3DF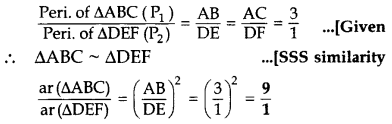
…[∵ The ratio of the areas of two similar ∆s is equal to the ratio of the squares of their corresponding sides
Question 11.
In the figure, EF || AC, BC = 10 cm, AB = 13 cm and EC = 2 cm, find AF. (2014)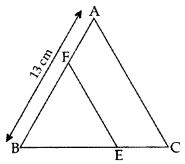
Solution:
BE = BC – EC = 10 – 2 = 8 cm
Let AF = x cm, then BF = (13 – x) cm
In ∆ABC, EF || AC … [Given
Question 12.
X and Y are points on the sides AB and AC respectively of a triangle ABC such that
Solution:
Given: 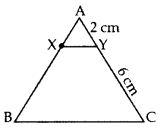
AX = 1K, AB = 4K
∴ BX = AB – AX
= 4K – 1K = 3K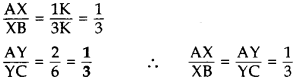
∴ XY || BC … [By converse of Thales’ theorem
Question 13.
In the given figure, ∠A = 90°, AD ⊥ BC. If BD = 2 cm and CD = 8 cm, find AD. (2012; 2017D)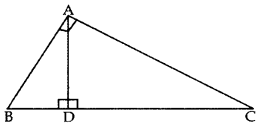
Solution:
∆ADB ~ ∆CDA …[If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle of a rt. ∆ to the hypotenuse then As on both sides of the ⊥ are similar to the whole D and to each other
∴
AD2 = BD , DC
AD2 = (2) (8) = 16 ⇒ AD = 4 cm
Question 14.
In ∆ABC, ∠BAC = 90° and AD ⊥ BC. Prove that AD\frac{B D}{A D}=\frac{A D}{C D} = BD × DC. (2013)
Solution:
In 1t. ∆BDA, ∠1 + ∠5 = 90°
In rt. ∆BAC, ∠1 + ∠4 = 90° …(ii)
∠1 + ∠5 = ∠1 + ∠4 …[From (i) & (ii)
.. ∠5 = ∠4 …(iii)
In ∆BDA and ∆ADC,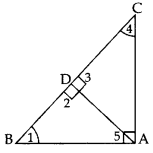
∠5 = 24 … [From (iii)
∠2 = ∠3 …[Each 90°
∴ ∆BDA ~ ∆ADC…[AA similarity
… [In ~ As corresponding BA sides are proportional
∴ AD2 = BD × DC
Question 15.
A 6.5 m long ladder is placed against a wall such that its foot is at a distance of 2.5 m from the wall. Find the height of the wall where the top of the ladder touches it. (2015)
Solution:
Let AC be the ladder and AB be the wall.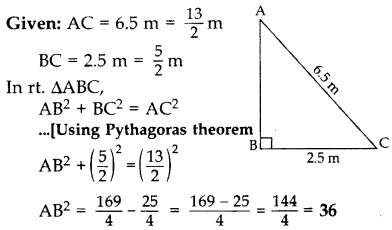
∴Required height, AB = 6 m
Question 16.
In the figure ABC and DBC are two right triangles. Prove that AP × PC = BP × PD. (2013)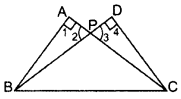
Solution: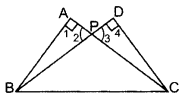
In ∆APB and ∆DPC,
∠1 = ∠4 … [Each = 90°
∠2 = ∠3 …[Vertically opp. ∠s
∴ ∆APB ~ ∆DPC …[AA corollary
⇒
∴ AP × PC = BP × PD
Question 17.
In the given figure, QA ⊥ AB and PB ⊥ AB. If AO = 20 cm, BO = 12 cm, PB = 18 cm, find AQuestion (2017OD)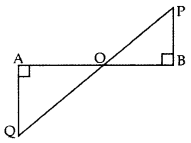
Solution: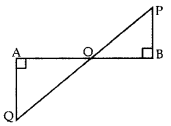
In ∆OAQ and ∆OBP,
∠OAQ = ∠OBP … [Each 90°
∠AOQ = ∠BOP … [vertically opposite angles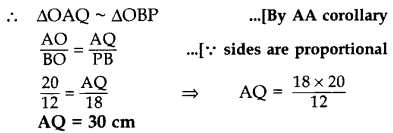
Triangles Class 10 Important Questions Short Answer-II (3 Marks)
Question 18.
In the given figure, CD || LA and DE || AC. Find the length of CL if BE = 4 cm and EC = 2 cm. (2012)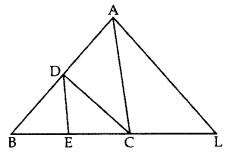
Solution:
In ∆ABL, CD || LA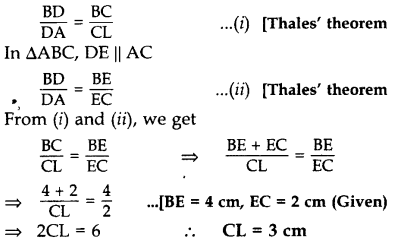
Question 19.
If a line segment intersects sides AB and AC of a ∆ABC at D and E respectively and is parallel to BC, prove that
Solution:
Given. In ∆ABC, DE || BC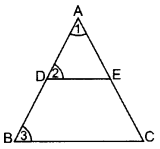
To prove.
Proof.
In ∆ADE and ∆ABC
∠1 = ∠1 … Common
∠2 = ∠3 … [Corresponding angles
∆ADE ~ ∆ABC …[AA similarity
∴
…[In ~∆s corresponding sides are proportional
Question 20.
In a ∆ABC, DE || BC with D on AB and E on AC. If
Solution:
Given: In a ∆ABC, DE || BC with D on AB and E
on AC and
To find:
Proof. Let AD = 3k,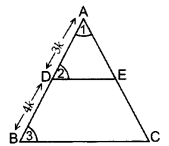
DB = 4k
∴ AB = 3k + 4k = 7k
In ∆ADE and ∆ABC,
∠1 = ∠1 …[Common
∠2 = ∠3 … [Corresponding angles
∴ ∆ADE ~ ∆ABC …[AA similarity
Question 21.
In the figure, if DE || OB and EF || BC, then prove that DF || OC. (2014)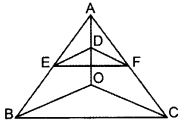
Solution:
Given. In ∆ABC, DE || OB and EF || BC
To prove. DF || OC
Proof. In ∆AOB, DE || OB … [Given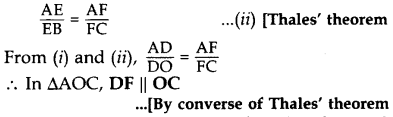
Question 22.
If the perimeters of two similar triangles ABC and DEF are 50 cm and 70 cm respectively and one side of ∆ABC = 20 cm, then find the corresponding side of ∆DEF. (2014)
Solution: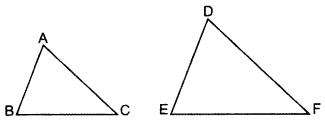
Given. ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF,
Perimeter(∆ABC) = 50 cm
Perimeter(∆DEF) = 70 cm
One side of ∆ABC = 20 cm
To Find. Corresponding side of ∆DEF (i.e.,) DE. ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF …[Given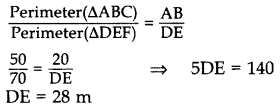
∴ The corresponding side of ADEF = 28 cm
Question 23.
A vertical pole of length 8 m casts a shadow 6 cm long on the ground and at the same time a tower casts a shadow 30 m long. Find the height of tower. (2014)
Solution: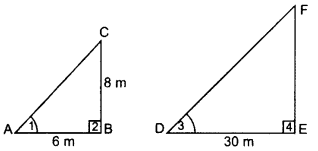
Let BC be the pole and EF be the tower Shadow AB = 6 m and DE = 30 m.
In ∆ABC and ∆DEF,
∠2 = ∠4 … [Each 90°
∠1 = ∠3 … [Sun’s angle of elevation at the same time
∆ABC ~ ∆DEF …[AA similarity
⇒
Question 24.
In given figure, EB ⊥ AC, BG ⊥ AE and CF ⊥ AE (2015)
Prove that:
(a) ∆ABG ~ ∆DCB
(b) 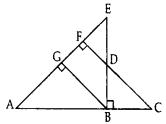
Solution: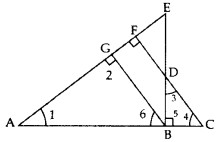
Given: EB ⊥ AC, BG ⊥ AE and CF ⊥ AE.
To prove: (a) ∆ABG – ∆DCB,
(b)
Proof: (a) In ∆ABG and ∆DCB,
∠2 = ∠5 … [each 90°
∠6 = ∠4 … [corresponding angles
∴ ∆ABG ~ ∆DCB … [By AA similarity
(Hence Proved)
∴ ∠1 = ∠3 …(CPCT … [In ~∆s, corresponding angles are equal
(b) In ∆ABE and ∆DBC,
∠1 = ∠3 …(proved above
∠ABE = ∠5 … [each is 90°, EB ⊥ AC (Given)
∆ABE ~ ∆DBC … [By AA similarity
… [In ~∆s, corresponding sides are proportional
∴
Question 25.
∆ABC ~ ∆PQR. AD is the median to BC and PM is the median to QR. Prove that
Solution:
∆ABC ~ ∆PQR … [Given
∠1 = ∠2 … [In ~∆s corresponding angles are equal
Question 26.
State whether the given pairs of triangles are similar or not. In case of similarity mention the criterion. (2015)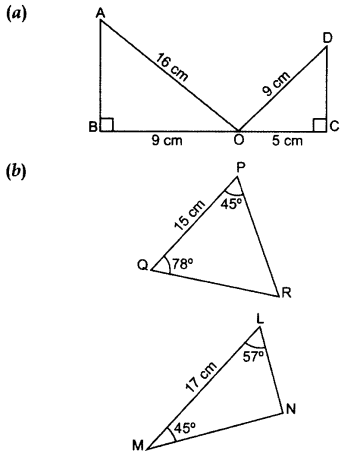
Solution: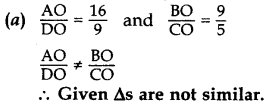
(b) In ∆PQR, ∠P + ∠Q + ∠ZR = 180° …[Angle-Sum Property of a ∆
45° + 78° + ∠R = 180°
∠R = 180° – 45° – 78° = 57°
In ∆LMN, ∠L + ∠M + ∠N = 180° …[Angle-Sum Property of a ∆
57° + 45° + ∠N = 180°
∠N = 180° – 57 – 45° = 78°
∠P = ∠M … (each = 45°
∠Q = ∠N … (each = 78°
∠R = ∠L …(each = 57°
∴ ∆PQR – ∆MNL …[By AAA similarity theorem
Question 27.
In the figure of ∆ABC, D divides CA in the ratio 4 : 3. If DE || BC, then find ar (BCDE) : ar (∆ABC). (2015)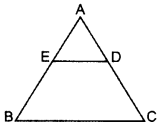
Solution:
Given:
D divides CA in 4 : 3
CD = 4K
DA = 3K
DE || BC …[Given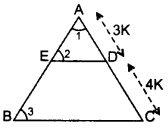
In ∆AED and ∆ABC,
∠1 = ∠1 …[common
∠2 = ∠3 … corresponding angles
∴ ∆AED – ∆ABC …(AA similarity
⇒
… [The ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the square of the ratio of their corresponding sides
⇒
Let ar(∆AED) = 9p
and ar(∆ABC) = 49p
ar(BCDE) = ar (∆ABC) – ar (∆ADE)
= 49p – 9p = 40p
∴
∴ ar (BCDE) : ar(AABC) = 40 : 49
Question 28.
In the given figure, DE || BC and AD : DB = 7 : 5, find \frac { ar\left( \triangle DEF \right) }{ ar\left( \triangle CFB \right) } [/latex] (2017OD)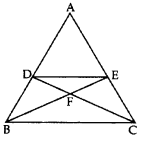
Solution:
Given: In ∆ABC, DE || BC and AD : DB = 7 : 5.
To find: 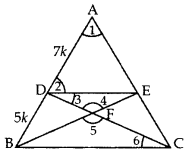
Proof: Let AD = 7k
and BD = 5k then
AB = 7k + 5k = 12k
In ∆ADE and ∆ABC,
∠1 = ∠1 …(Common
∠2 = ∠ABC … [Corresponding angles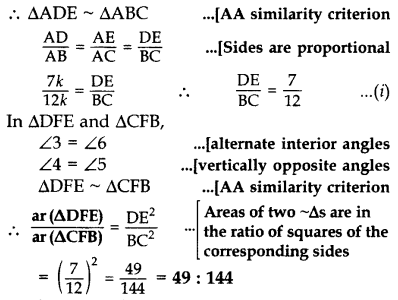
Question 29.
In the given figure, the line segment XY is parallel to the side AC of ∆ABC and it divides the triangle into two parts of equal areas. Find the ratio 
Solution:
We have XY || AC … [Given
So, ∠BXY = ∠A and ∠BYX = ∠C …[Corresponding angles
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆XBY …[AA similarity criterion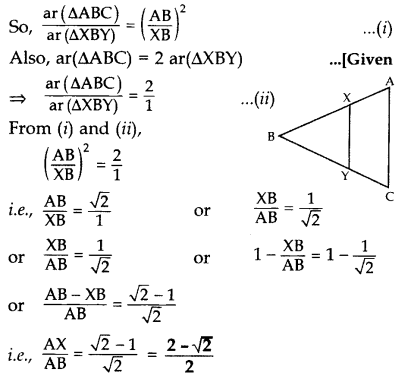
Question 30.
In the given figure, AD ⊥ BC and BD = 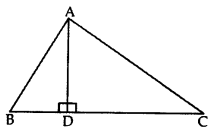
Solution:
BC = BD + DC = BD + 3BD = 4BD
∴
In rt. ∆ADB, AD2 = AB2 – BD2 ….(ii)
In rt. ∆ADC, AD2 = AC2 – CD2 …(iii)
From (ii) and (iii), we get
AC2 – CD2 = AB2 – BD2
AC2 = AB2 – BD2 + CD2
∴ 2AC2 = 2AB2 + BC2 (Hence proved)
Question 31.
In the given figure, ∆ABC is right-angled at C and DE ⊥ AB. Prove that ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE and hence find the lengths of AE and DE. (2012, 2017D)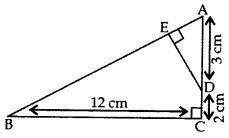
Solution:
Given: ∆ABC is rt. ∠ed at C and DE ⊥ AB.
AD = 3 cm, DC = 2 cm, BC = 12 cm
To prove:
(i) ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE; (ii) AE = ? and DE = ?
Proof. (i) In ∆ABC and ∆ADE,
∠ACB = ∠AED … [Each 90°
∠BAC = ∠DAE …(Common .
∴ ∆ABC ~ ∆ADE …[AA Similarity Criterion
(ii) ∴
…..[In rt. ∆ACB, … AB2 = AC2 + BC2 (By Pythagoras’ theorem)
= (5)2 + (12)2 = 169
∴ AB = 13 cm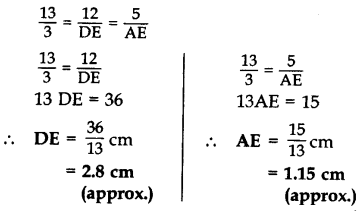
Question 32.
In ∆ABC, if AP ⊥ BC and AC2 = BC2 – AB2, then prove that PA2 = PB × CP. (2015)
Solution: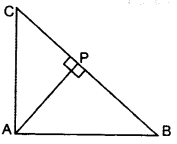
AC2 = BC2 – AB2 …Given
AC2 + AB2 = BC2
∴ ∠BAC = 90° … [By converse of Pythagoras’ theorem
∆APB ~ ∆CPA
[If a perpendicular is drawn from the vertex of the right angle of a triangle to the hypotenuse then As on both sides of the perpendicular are similar to the whole triangle and to each other.
∴
∴ PA2 = PB. CP (Hence Proved)
Question 33.
ABCD is a rhombus. Prove that AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2 = AC2 + BD2. (2013)
Solution:
Given. In rhombus ABCD, diagonals AC and BD intersect at O.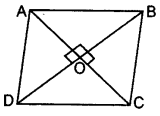
To prove: AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2 = AC2 + BD2
Proof: AC ⊥ BD [∵ Diagonals of a rhombus bisect each other at right angles
∴ OA = OC and
OB = OD
In rt. ∆AOB,
AB2 = OA2 + OB2 … [Pythagoras’ theorem
AB2 =
AB2 =
4AB2 = AC2 + BD2
AB2 + AB2 + AB2 + AB2 = AC2 + BD2
∴ AB2 + BC2 + CD2 + DA2 = AC2 + BD2
…[∵ In a rhombus, all sides are equal
Question 34.
The diagonals of trapezium ABCD intersect each other at point o. If AB = 2CD, find the ratio of area of the ∆AOB to area of ∆COD. (2013)
Solution:
In ∆AOB and ∆COD, … [Alternate int. ∠s
∠1 = ∆3
∠2 = ∠4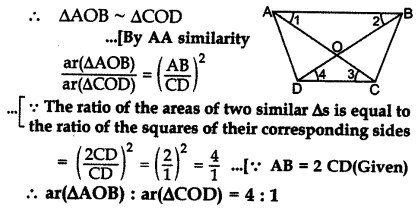
Question 35.
The diagonals of a quadrilateral ABCD intersect each other at the point O such that
Solution:
1st method.
Given: Quadrilateral ABCD in which
AC and BD intersect each other at 0.
Such that
To prove: ABCD is a trapezium
Const.: From O, draw OE || CD.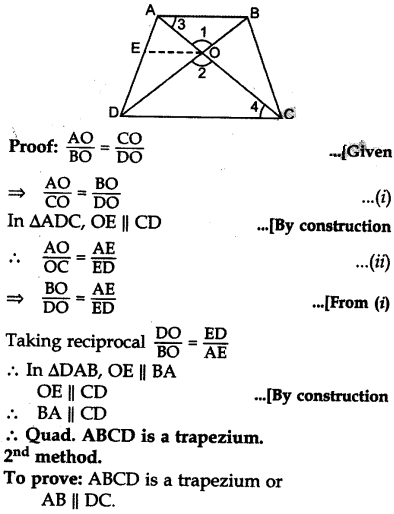

But these are alternate interior angles
∴ AB || DC Quad. ABCD is a trapezium.
Triangles Class 10 Important Questions Long Answer (4 Marks).
Question 36.
In a rectangle ABCD, E is middle point of AD. If AD = 40 m and AB = 48 m, then find EB. (2014D)
Solution: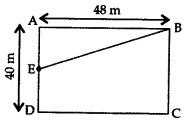
E is the mid-point of AD …[Given
AE =
∠A = 90° …[Angle of a rectangle
In rt. ∆BAE,
EB2 = AB2 + AE2 …[Pythagoras’ theorem
= (48)2 + (20)2
= 2304 + 400 = 2704
∴ EB =
Question 37.
Let ABC be a triangle and D and E be two points on side AB such that AD = BE. If DP || BC and EQ || AC, then prove that PQ || AB. (2013)
Solution: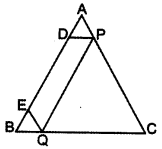
In ∆ABC,
DP || BC
and EQ || AC … [Given
Now, in ∆ABC, P and Q divide sides CA and CB respectively in the same ratio.
∴ PQ || AB
Question 38.
In the figure, ∠BED = ∠BDE & E divides BC in the ratio 2 : 1.
Prove that AF × BE = 2 AD × CF. (2015)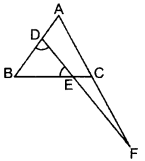
Solution:
Construction:
Draw CG || DF
Proof: E divides
BC in 2 : 1.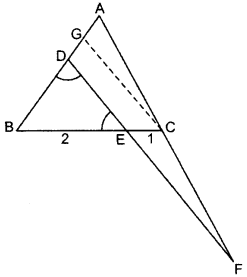
Question 39.
In the given figure, AD = 3 cm, AE = 5 cm, BD = 4 cm, CE = 4 cm, CF = 2 cm, BF = 2.5 cm, then find the pair of parallel lines and hence their lengths. (2015)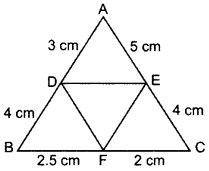
Solution:
Question 40.
If sides AB, BC and median AD of AABC are proportional to the corresponding sides PQ, QR and median PM of PQR, show that ∆ABC ~ ∆PQR. (2017OD)
Solution: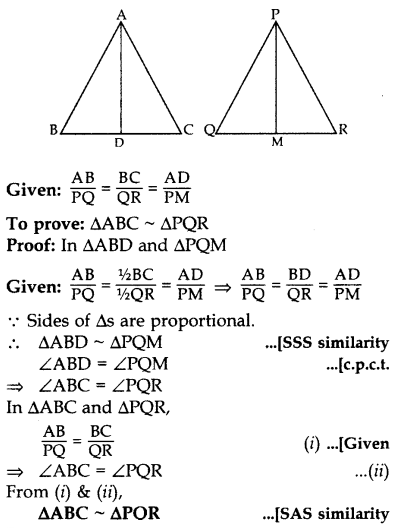
Question 41.
Prove that the ratio of the areas of two similar triangles is equal to the ratio of the squares of their corresponding sides. (2012)
Solution:
Given: ∆ABC ~ ∆DEF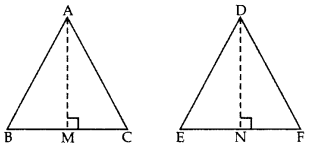


Question 42.
State and prove converse of Pythagoras theorem. Using the above theorem, solve the following: In ∆ABC, AB = 6
Solution:
Part I:
Statement: Prove that, in a triangle, if square of one side is equal to the sum of the squares of the other two sides, then the angle opposite the first side is a right angle.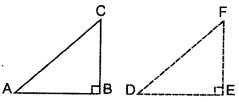
To prove: ∠ABC = 90°
Const.: Draw a right angle ∆DEF in which DE = BC and EF = AB.
Proof: In rt. ∆ABC,
AB2 + BC2 = AC2 …(i) Given
In rt. ∆DEF
DE2 + EF2 = DF2 … [By Pythagoras’ theorem
BC2 + AB2 = DF2…(ii)…[∵ DE = BC; EF = AB
From (i) and (ii), we get
AC2 = DF2 = AC = DF
Now, DE = BC …[By construction
EF = AB …[By construction
DF = AC … [Proved above :
∴ ∆DEF = ∆ABC … (SSS congruence :
∴ ∠DEF = ∠ABC …[c.p.c.t.
∵ ∠DEF = 90° ∴ ∠ABC = 90°
Given: In rt. ∆ABC,
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
AB2 + BC2 = (6
= 108 + 36 = 144 = (12)2
AB2 + BC2 = AC2 ∴ ∠B = 90° … [Above theorem
Question 43.
In the given figure, BL and CM are medians of a triangle ABC, right angled at A. Prove that: 4(BL2 + CM2) = 5BC2 (2012)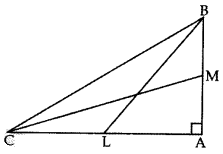
Solution:
Given: BL and CM are medians of ∆ABC, right angled at A.
To prove: 4(BL2 + CM2) = 5 BC2
Proof: In ∆ABC, BC2 = BA2 + CA2 …(i)
In ∆BAL,
BL2 = BA2 + AL2 …[Pythagoras’ theorem
BL2 = BA2 +
BL2 = BA2+
⇒ 4BL2 = 4BA2 + CA2 …(ii)
Now, In ∆MCA,
MC2 = CA2 + MA2 …[Pythagoras’ theorem
MC2 = CA22 +
MC2 = CA2 +
4MC2 = 4CA2 + BA2
Adding (ii) and (iii), we get
4BL2 + 4MC2 = 4BA2 + CA2 + 4CA2+ BA2 …[From (ii) & (iii)
4(BL2 + MC2) = 5BA2 + 5CA2
4(BL2 + MC2) = 5(BA2 + CA2)
∴ 4(BL2 + MC2) = 5BC2 … [Using (1)
Hence proved.
Question 44.
In the given figure, AD is median of ∆ABC and AE ⊥ BC. (2013)
Prove that b2 + c2 = 2p2 + 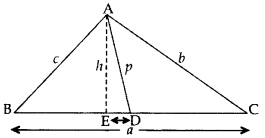
Solution: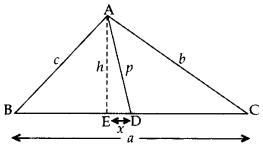
Proof. Let ED = x
BD = DC =
In rt. ∆AEC, AC2 = AE2 + EC2 …..[By Pythagoras’ theorem
b2 = h2 + (ED + DC)2
b2 = (p2 – x2) + (x =
…[∵ In rt. ∆AED, x2 + h2 = p2 ⇒ h2 = p2 – x2 …(i)
b2 = p2 – x2 + x2 +
b2 = p2 + ax +
In rt. ∆AEB, AB2 = AE2 + BE2 … [By Pythagoras’ theorem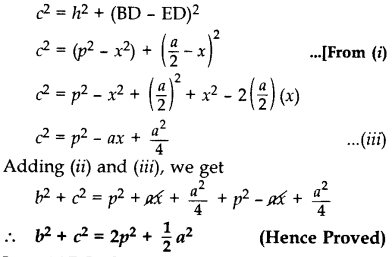
Question 45.
In a ∆ABC, the perpendicular from A on the side BC of a AABC intersects BC at D such that DB = 3 CD. Prove that 2 AB2 = 2 AC2 + BC2. (2013; 2017OD)
Solution:
In rt. ∆ADB,
AD2 = AB2 – BD2 …(i) [Pythagoras’ theorem
In rt. ∆ADC,
AD2 = AC2 – DC2 …(ii) [Pythagoras’ theorem
From (i) and (ii), we get
AB2 – BD2 = AC2 – DC2
AB2 = AC2 + BD2 – DC2
Now, BC = BD + DC
= 3CD + CD = 4 CD …[∵ BD = 3CD (Given)
⇒ BC2 = 16 CD2 …(iv) [Squaring
Now, AB2 = AC2 + BD2 – DC2 …[From (iii)
= AC2 + 9 DC2 – DC2 ….[∵ BD = 3 CD ⇒ BD2 = 9 CD2
= AC2 + 8 DC2
= AC2 +
= AC2 +
∴ 2AB2 = 2AC2 + BC2 … [Proved
Question 46.
In ∆ABC, altitudes AD and CE intersect each other at the point P. Prove that: (2014)
(i) ∆APE ~ ∆CPD
(ii) AP × PD = CP × PE
(iii) ∆ADB ~ ∆CEB
(iv) AB × CE = BC × AD
Solution: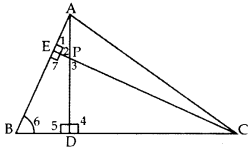
Given. In ∆ABC, AD ⊥ BC & CE ⊥ AB.
To prove. (i) ∆APE ~ ∆CPD
(ii) AP × PD = CP × PE
(iii) ∆ADB ~ ∆CEB
(iv) AB × CE = BC × AD
Proof: (i) In ∆APE and ∆CPD,
∠1 = ∠4 …[Each 90°
∠2 = ∠3 …[Vertically opposite angles
∴ ∆APE ~ ∆CPD …[AA similarity
(ii)
∴ AP × PD = CP × PE
(iii) In ∆ADB and ∆CEB,
∠5 = ∠7 …[Each 90°
∠6 = ∠6 …(Common
∴ ∆ADB ~ ∆CEB …[AA similarity
(iv) ∴
∴ AB × CE = BC × AD
Question 47.
In the figure, PQR and QST are two right triangles, right angled at R and T resepctively. Prove that QR × QS = QP × QT. (2014)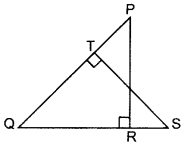
Solution:
Given: Two rt. ∆’s PQR and QST.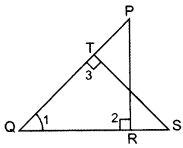
To prove: QR × QS = QP × QT
Proof: In ∆PRQ and ∆STQ,
∠1 = ∠1 … [Common
∠2 = ∠3 … [Each 90°
∆PRQ ~ ∆STO …(AA similarity
∴
∴ QR × QS = QP × QT (Hence proved)
Question 48.
In the given figure, ABC and DBC are two triangles on the same base BC. If AD intersects BC at O, show that 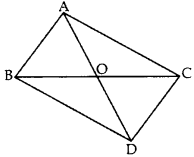
Solution:
Given: ABC and DBC are two As on the same base BC. AD intersects BC at O.
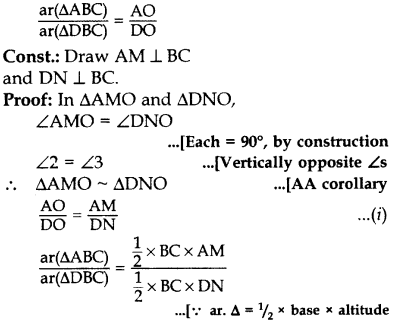
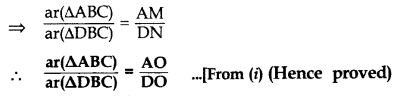
To prove: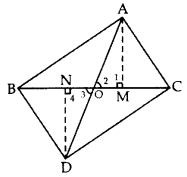
Question 49.
Hypotenuse of a right triangle is 25 cm and out of the remaining two sides, one is longer than the other by 5 cm. Find the lengths of the other
two sides. (2013)
Solution:
Let Base, AB = x cm
Then altitude, BC = (x + 5) cm
In rt. ∆,
By Pythagoras’ theorem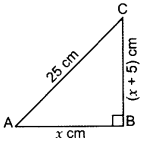
AB2 + BC2 = AC2
⇒ (x)2 + (x + 5)2 = 252
⇒ x22 + x2 + 10x + 25 – 625 = 0
⇒ 2x2 + 10x – 600 = 0
⇒ x2 + 5x – 300 = 0 … [Dividing both sides by 2
⇒ x2 + 20x – 15x – 300 = 0
⇒ x(x + 20) – 15(x + 20) = 0
(x – 15)(x + 20) = 0
x – 15 = 0 or x + 20 = 0
x = 15 or x = -20
Base cannot be -ve
∴ x = 15 cm
∴ Length of the other side = 15 + 5 = 20 cm
Two sides are = 15 cm and 20 cm
Question 50.
In Figure, AB ⊥ BC, FG ⊥ BC and DE ⊥ AC. Prove that ∆ADE ~ ∆GCF. (2016 OD)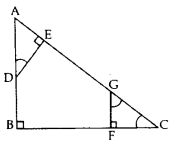
Solution:
In rt. ∆ABC,
∠A + ∠C = 90° …(i)
In rt. ∆AED,
∠A + ∠2 = 90°
From (i) and (ii), ∠C = ∠2
Similarly, ∠A = ∠1
Now in ∆ADE & ∆GCF
∠A = 1 … [Proved
∠C = 2 … [Proved
∠AED = ∠GFC … [rt. ∠s
∴ ∆ADE – ∆GCF …(Hence Proved)
I hope this helps you in excelling in your academics. Please check out other important PYQs of Mathematics. If you have any queries, please do let me know in the comments section.
Thanking You.
Comments
Post a Comment